Looking Back at Climate Change

History allows us to learn from the past, reflect on the present, and prepare for our future. Climate change has occurred for billions of years, and we can now look back at the last 1000 years. What we take from the past millennium could severely alter our future. The choice is ours!!!
Eruptions Influencing Climate.

The article ‘Causes of climate change over the historical record’ reviewed current understanding, knowledge, and research on climate change from 1750 to 2019 [1]. The article details how there has been a clear warming trend since the Industrial Revolution; however, this trend was interrupted when the 19th century was slightly cooler than the 18th century [1]. The reason for this disruption was due to the cooling effects caused by volcanic eruptions in the 1800s [1], including Mount Tambora (1815). The gas and ash released from these eruptions block the sun’s radiation from reaching the surface, resulting in a cooling effect. However, once the cooling effects dwindled, the 1900s saw the rapid rise in temperatures continue [1] as radiation from the sun reached the surface once more. There is a pattern of strong warming trends occurring after the cooling effects from eruptions diminish [1].
The temperature rise was once again interrupted briefly due to volcanic eruptions such as Mount Agung (1963), causing a brief cooling period between 1950 and 1980 [1]. However, just because an eruption occurs does not mean it will have a significant influence on the climate. This is displayed from 1980 to 2012 [1], when volcanic eruptions did occur; however, the warming trend continued drastically [1]. Nevertheless, this indicates that strong and large volcanic eruptions have and will continue to have a major influence on climate.
History Solidifies the Effects of Greenhouse Gases.
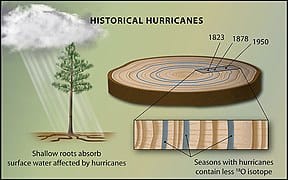
History has also provided various evidence on how greenhouse gases are significantly correlated with climate. This includes physical environmental evidence (paleoclimate research) [1] such as tree rings (Figure 1) and ice cores (Figure 2) that suggests that temperature increases are a response to rises in greenhouse gases throughout the Northern Hemisphere [1].

The Industrial Revolution and human activities since are credited with this increase in greenhouse gases, which has resulted in them having the strongest influence on global warming [1]. In addition, the continuous burning of fossil fuels has led to an increase in anthropogenic aerosols (human-created pollutants), which has had a significant effect on temperature increases, especially in the 1980s [1]. Interestingly, aerosols still seem to have a strong effect even when the amount produced has decreased in Europe and North America; however, they continue to increase in Asia and South America [1].

Why Does Aerosol Production Vary?
A reason for this could be that European and North American nations are mostly developed societies that have easier access to advanced and sustainable energy. However, Asia and South America consist of fast-growing nations that need to produce high amounts of energy to grow; however, they struggle to acquire renewable energy, thus resulting in higher burning of fossil fuels.
Limitations of Aerosol Data.
Aerosols may have a strong impact on global warming; however, the article acknowledges that it is difficult to comprehend the impact of natural aerosols due to the variety and uncertainty of measuring its impact [1].
The Ozone Hole’s Impact on Climate.
Furthermore, the ozone layer has been recognised as a significant issue by climate activists, but what does history tell us? Well, the thinning of the ozone layer does significantly influence the impact of solar forcing (the amount of energy from the sun that reaches Earth compared to the amount of energy that leaves Earth), as the thinner the ozone layer, the more radiation such as UV will reach the surface. However, there is limited evidence that solar forcing has a significant effect on temperature, with various studies reporting that it only has a moderate impact on global warming [1]. It's fascinating how the thinning of the ozone layer was a significant part of climate change advocacy, yet the results mentioned in this article indicate that it wasn’t a critical factor [1].
Other Revelations.
The last 1000 years have also shown that global warming has significant effects on oceans and rain patterns [1]. But what are the consequences?
Fascinatingly, land usage has also been reported to greatly affect temperature [1], but why?
These are only a couple of the various factors of climate change that have been exhibited in the past 1000 years, and an in-depth explanation is needed to answer these questions.
Data Acknowledgements.
It must be acknowledged that some of the data is based on observations [1], which are not always considered accurate or reliable; thus, some of the models and simulations that produced these results are not necessarily 100% accurate. Furthermore, models are only simulations that are not definite. However, the results produced are based on strong evidence and consistent scientific methods; thus, they should be taken with high regard.
We MUST Learn from the Past!
Therefore, as we look at the past 1000 years, we can see various patterns of climate change that are influencing the current global warming situation; however, it is evident that human contributions are causing a significant temperature rise that has not been seen in the past 1000 years. What we will do with the information is up to us!
References
Reference paper “Causes of climate change over the historical record”
1. Hegerl, G.C., Brönnimann, S., Cowan, T., Friedman, A.R., Hawkins, E., Iles, C., Müller, W., Schurer, A. and Undorf, S., 2019. Causes of climate change over the historical record. Environmental Research Letters, 14(12), p.123006.
