Explaining the Phases of the Moon

The Moon appears to take on a new shape every night, known as lunar phases.
The article “Moon Phases—NASA Science” will help us identify and explore the Moon's different phases.
What Causes the Moon to Shine?
We can see the Moon due to the Sun's light reflecting off the Moon’s surface, which results in moonlight [1]. It takes the Moon 29.5 days to orbit Earth [1], and during this cycle, the angle between the Sun, Earth, and Moon shifts, changing how much of the Moon is lit.
Lunar Phases
🌑 New Moon

This is the phase where the Moon is positioned between the Sun and Earth, meaning that the sunlit side is facing away from us, making the Moon invisible in the night sky [1].
🌒 Waxing Crescent

A small curved sliver becomes visible [1].
🌓 First Quarter (Half Moon)

We can now see half of the Moon.
🌔 Waxing Gibbous

More than half the Moon is visible and appears brighter [1].
🌕 Full Moon

The entire sunlit side of the Moon faces Earth, making it a 'full moon.'[1].
🌖 Waning Gibbous

Most of the Moon is visible, besides a small sliver [1].
🌗 Last Quarter
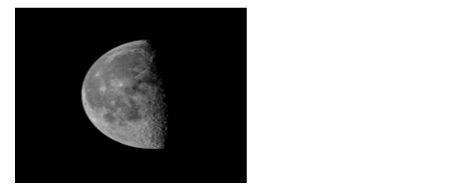
The Moon returns to its ‘half-moon’ state [1]
🌘 Waning Crescent

The Moon is almost back to its ‘invisible phase,’ and all we see is a thin curve [1].
Other Interesting Facts about The Moon
Shaky Moon
Besides our changing night sky, scientists and sky watchers have observed that the Moon appears to "twist, nod, and roll slightly," a movement called liberation [1]. This nod occurs due to the 5-degree tilt in the Moon's orbit [1]. You can see a video of this effect here: NASA Moon Phases.
Earthshine
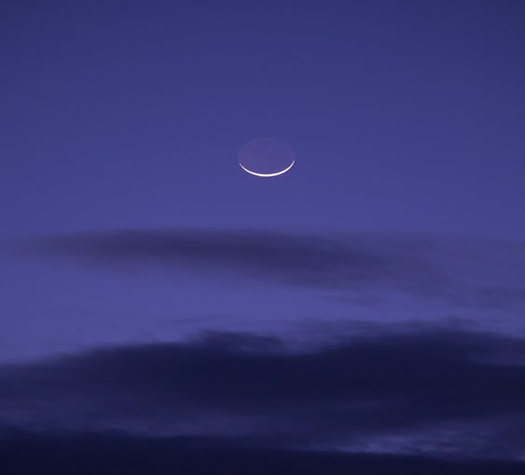

Occasionally, in the crescent phase, the darkened part of the Moon appears dimly lit [1]. This is due to Earthshine, where sunlight reflects off the Earth's surface onto the face of the Moon [1]. At this point in the Moon cycle, the Earth is nearly full from the Moon’s perspective; thus, the light reflected can dimly illuminate this darkened part [1].
Why Can I See the Moon During the Day?
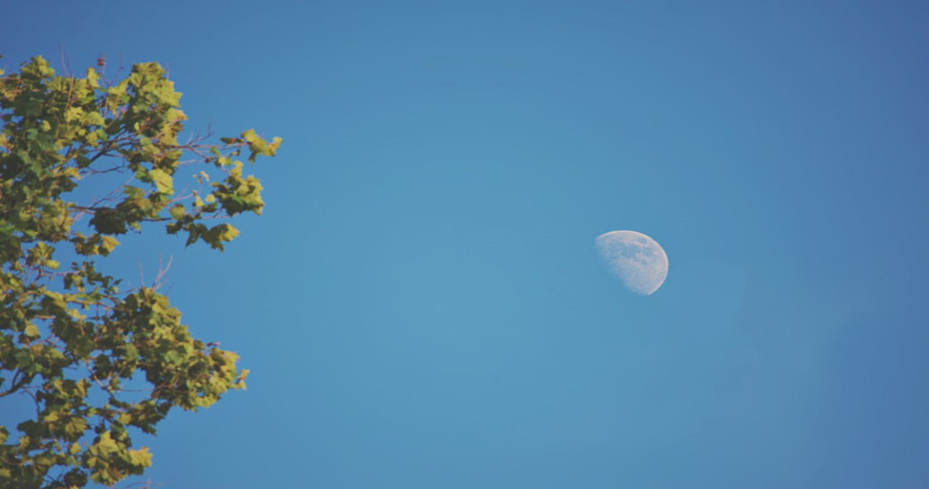

You may have noticed that the Moon is visible during the day. The best time to see this is during the first and last quarter phases, about 90 degrees from the Sun in the sky, allowing enough sunlight to reflect off the Moon for us to see it during the day [1]. It is possible to see the Moon during the day in all phases, except the ‘New Moon' [1].
We Can Only See One Side of the Moon.
Tidal locking is a process that causes the Moon to take the same amount of time to rotate as it does to orbit Earth; this is called synchronous rotation [1]. As a result, we always see the same side of the Moon known as the near side [1].
Our Lunar Light
The ever-changing faces of the Moon are a fascinating aspect of our night sky, allowing us to explore the relationship between Earth, the Moon, and the Sun.
References
Reference paper “Moon phases - NASA science. Available at: https://science.nasa.gov/moon/moon-phases/ (Accessed: 12 February 2025).”
